- Home
- Foot & Ankle Conditions
- Metatarsalgia (ball of foot pain)
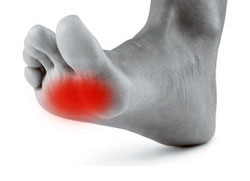
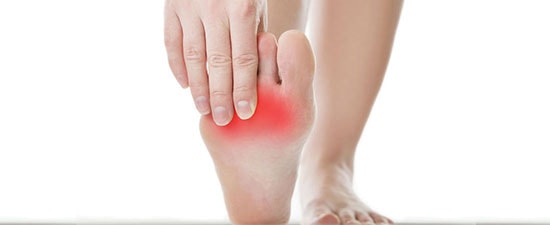
Metatarsalgia: symptoms, causes and treatments
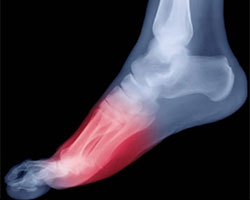
What is Metatarsalgia?
Metatarsalgia often referred to as "ball of the foot pain" or a "stone bruise" is not so much a condition but a general term describing a group of foot problems whose symptoms are caused by several conditions.
In some cases, there can be more than one condition causing metatarsalgia symptoms. This is just one of several reasons why a proper diagnosis can be challenging and why the experience of your doctor is such a critical part of diagnosis and getting a successful treatment plan from the start.
-
Foot and Ankle Surgeon at University Foot and Ankle Institute
Dr. Justin Franson, DPM, is a Board Certified Podiatric Foot and Ankle Specialist and Diplomate of the American Board of Podiatric Surgery. He attended the School College of Podiatric Medicine in Chicago, graduating in 2001. Dr. Franson then accepted a three-year residency program at the Greater Los Angeles VA and UCLA County Hospital.
Dr. Franson specializes in several areas including total ankle replacement and sports medicine. Treating athletes and weekend warriors like himself brings him a lot of joy. Dr. Franson keeps active with running marathons, triathlons, hiking, basketball, and golf.
Metatarsalgia articles from our blog
 Dr. Avanti Redkar has been treating me since I crushed my heel. Dr. Redkar is very detailed and has a fantastic bedside manner....Pete L.
Dr. Avanti Redkar has been treating me since I crushed my heel. Dr. Redkar is very detailed and has a fantastic bedside manner....Pete L. Great experience. Great communication. Great direction for my care. Very happy I chose to go with this particular doctor and o...Christopher R.
Great experience. Great communication. Great direction for my care. Very happy I chose to go with this particular doctor and o...Christopher R. Great service and care. Highly recommend Dr. Franson.David B.
Great service and care. Highly recommend Dr. Franson.David B. If you have to go see a Doctor than this is a great experience.Frank M.
If you have to go see a Doctor than this is a great experience.Frank M. My doctor was great. Really greatRudolph B.
My doctor was great. Really greatRudolph B. Good.David E.
Good.David E. Your Santa Barbara office and Dr. Johnson always give me excellent care!Jayne A.
Your Santa Barbara office and Dr. Johnson always give me excellent care!Jayne A. Dr. Baravarian misdiagnosed a simple issue. I came back a week later to show that the "callus" he diagnosed was actually NOT, a...Omar N.
Dr. Baravarian misdiagnosed a simple issue. I came back a week later to show that the "callus" he diagnosed was actually NOT, a...Omar N. Dr. Gina Nalbadian was amazing!! I came in with an emergency foot situation and she had wonderful bedside manner and resolved m...Danielle C.
Dr. Gina Nalbadian was amazing!! I came in with an emergency foot situation and she had wonderful bedside manner and resolved m...Danielle C. I was frustrated that after 3 weeks I still hadn’t heard back about my PT referral status. And I did sit in a room for over 30 ...Sarah C.
I was frustrated that after 3 weeks I still hadn’t heard back about my PT referral status. And I did sit in a room for over 30 ...Sarah C. Hoping for the best. Never can be certain about the outcome of toenail laser therapy.Victor S.
Hoping for the best. Never can be certain about the outcome of toenail laser therapy.Victor S. I’m very pleased with Dr. Kelman.Alan S.
I’m very pleased with Dr. Kelman.Alan S.